2020-10 upd: we reached the first fundraising goal and rented a server in Hetzner for development! Thank you for donating !
Attention! I apologize for the automatic translation of this text. You can improve it by sending me a more correct version of the text or fix html pages via GITHUB repository.
Attention! Current pages describe CBSD version 13.0.x. If you are using an older version, please update first.
Please note: these commands support the mask (wildcard) as a jname, for example: jname='*', jname='ja*l*'
bhyve virtual disk
Commands: bconfig, bset, bhyve-dsk
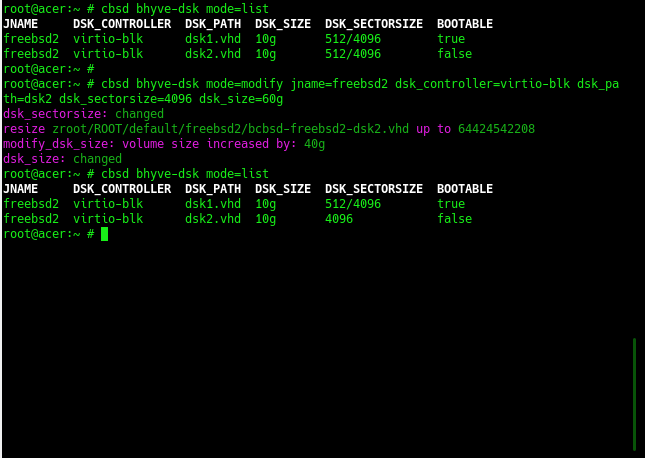
% cbsd bhyve-dsk mode=modify dsk_sectorsize=512/4096 jname='*'
Description:
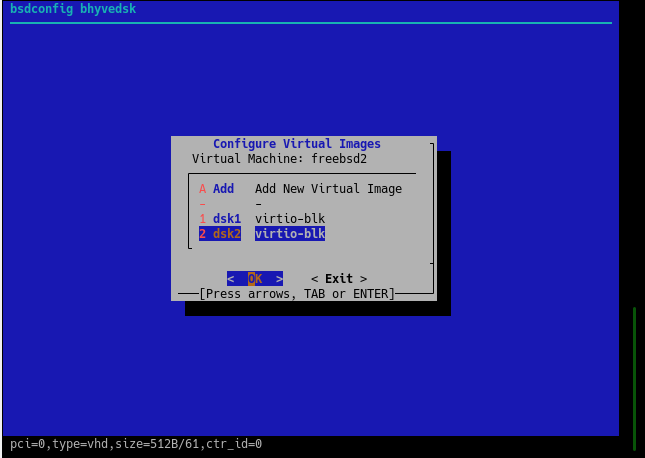
To work with bhyve virtual disks, use the cbsd bhyve-dsk command or the cbsd bconfig dialog with the bhyvedsk submenu.
list of disk
To list virtual disks, use:
% cbsd bhyve-dsk mode=list
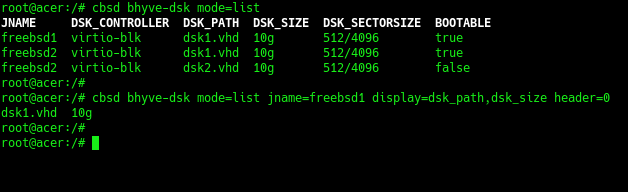
You can adjust the amount of information through arguments header=0 и display=
adding drives
To add a new virtual disk, use the command:
% cbsd bhyve-dsk mode=attach dsk_controller=XXX dsk_size=YYY
, where:
- XXX - type of controller: virtio-blk or ahci-hd
- YYY - Desired disk space, for example: 10g. An example of a command that will create and connect a new virtual disk to the freebsd1 virtual machine:
% cbsd bhyve-dsk mode=attach jname=freebsd1 dsk_controller=virtio-blk dsk_size=10g
detaching and remove drives
If you want to disconnect a virtual disk WITHOUT physically deleting the image, use:
% cbsd bhyve-dsk mode=detach dsk_controller=XXX dsk_path=YYY
, where:
- XXX - The type of disk controller you are disconnecting. Must match what you see through mode=list
- YYY - The name of disk you are disconecting. Must match what you see through mode=list
After disconnecting, do not lose sight of your drive, as it is no longer registered in CBSD
If you want to disconnect and at the same time destroy the virtual disk, use the command:
% cbsd bhyve-dsk mode=remove dsk_controller=XXX dsk_path=YYY
, where:
- XXX - The type of disk controller you are delete. Must match what you see through mode=list
- YYY - The name of disk you are delete. Must match what you see through mode=list
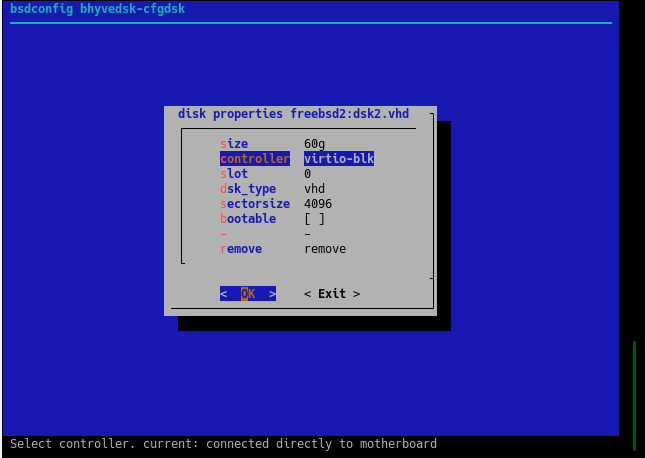
modification of properties of virtual disks
To modify the parameters of virtual disks, use the command:
% cbsd bhyve-dsk mode=modify jname=ZZZ dsk_controller=XXX dsk_path_YYY [param=value]
, where:
- ZZZ - VM name
- XXX - The type of disk controller you are modify. Must match what you see through mode=list
- YYY - The name of disk you are modify. Must match what you see through mode=list
Depending on the version of CBSD, the type of installation and the file system used, the set of parameters with which you can operate may differ
Basic parameters that are available on any file system:
- bootable - set disk as bootable, e.g: 1
- dsk_sectorsize - change disk sectorsize, e.g: 512,512/4096,4096 [*]
- dsk_size - increase the volume size of a virtual disk, for example: 30g (set size to 30Гб ),+10g (increase existing disk capacity by 10 GB) [**]
___
[*]
- choose the correct sectorsize before formatting the disk, because the data recorded with one value of sectorsize will not be available with another.
- when you specify a value through '/', the number on the left means logical sectorsize, the value on the right means physical sectors. Most preferred value: 512/4096 or 4096.
- you can reassign the default value in CBSD globally via bhyve-default-default.conf or in an individual virtual machine profile.
[**]
- virtual machines using cloud-init will resize/expand the guest disk automatically.
If you do not use cloud-init, in addition to increasing the physical medium, you will need to expand the guest file system yourself through the appropriate utilities.
customization ZFS/zvol properties
The ZFS file system has a rich selection of settings and optimizations. Since CBSD works intensively with the automatic creation of large numbers of ZFS file systems and ZVOL volumes and various settings, you can change the settings that CBSD will use in these operations.
You can change the default settings for ZFS datasets and ZVOL volumes through the zfs.conf configuration file. For example, you can enable compression for GOLD images of cloud-init, change recordsize, volblockmodesize, etc.